|
Have we ever asked ourselves a simple question – What do Google, McDonald's and Harry Potter have in common? The answer is even simpler than the question – these magic words are known by most of us. But if we try to find out the answer with a broader approach we will see that, all these brand names have an impact on the global market not only significantly but also effectively. Behind their global success there are many factors such as – product quality, marketing, product acceptability, service, customer relation and many more; but one more common significant factor these multinational business houses also share – a term called Localization. Localization has made it possible for them to extend their business beyond the border of their actual origin and to engrave their prominent presence throughout the map of our global village. In this context a brief introduction to the terms like Localization, Internationalization, and Globalization is eventually necessary and we will also see why and how these concepts have inevitably changed the way of doing many conventional businesses.
LOCALIZATION – THE ‘WHAT’ FACTOR – A DEFINED CONCEPT
As we know, for a conceptual term, if the underlying concept is not very simple in nature or has not been practiced generally, then it might lead us to many misconceptions or sometimes it might become difficult to define it also. A similar scenario is observed in case of Localization also. Unfortunately, till now some of us do not exactly know what Localization is all about, or in many cases even people engaged or related to software industry often consider that it is somewhat synonymous to the term Translation.
Let us find out a conventional definition which will not only define the underlying concept of Localization but will also help us to understand what localization is.
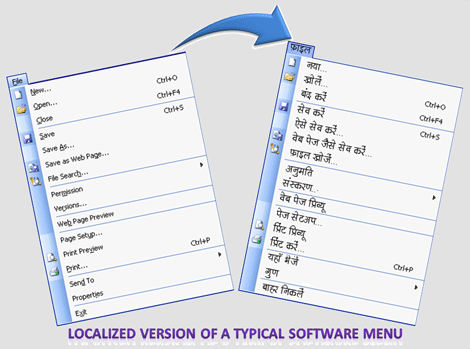
In simple words, Localization – often shortened as L10N – is the process of adapting a product or service to a particular language, culture, and locale. This systematic process combines translations and cultural adaptations of products and services to make them suitable and understandable to a specific culture, location and market niche and more importantly it provides the local ‘Look & feel’ which is desired by the end-user of that particular locale.
On the other hand, Translation is one of the several services that contribute to the localization process. So in addition to translation, there are many serious steps or responsibilities that come under the localization process, which might include adapting graphical content to the target markets, modifying content layout to fit the translated content, converting to local currencies, using locale specific formats for dates, addresses, and phone numbers, addressing local regulations and many more.
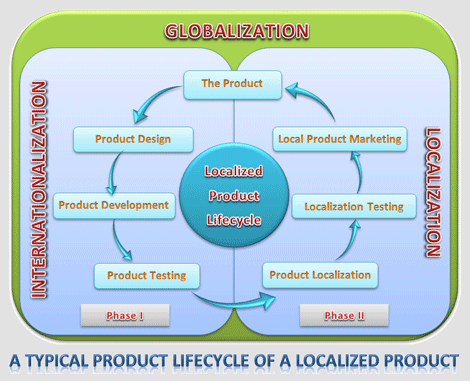 Internationalization – often shortened as I18N – is the process of designing a product to accommodate multiple languages and markets, so that it can be adapted to desired languages and regions without any engineering changes to the product. This preparatory process of priming the product can save considerable time and effort at the time of localization of the product to make it reachable to the global market. So in simple words the basic goal of Internationalization is to make the product localizable. Internationalization – often shortened as I18N – is the process of designing a product to accommodate multiple languages and markets, so that it can be adapted to desired languages and regions without any engineering changes to the product. This preparatory process of priming the product can save considerable time and effort at the time of localization of the product to make it reachable to the global market. So in simple words the basic goal of Internationalization is to make the product localizable.
Globalization – often shortened as G11N – is the cumulative work of translating and integrating all business functions – from processes to products and communications – to make a company ready for the global marketplace. Hence, Internationalization, Localization and all other related processes come under Globalization.
Note: The terms Globalization, Localization, Internationalization are frequently abbreviated to the numeronyms as G11N, L10N and I18N respectively, where the middle number, for example, 10 in case of L10N stands for the number of letters between the first and last letter of Localization i.e. L and N respectively.
LOCALIZATION – THE ‘HOW’ FACTOR – GO GLOBAL BY GOING LOCAL
The above definitions may be useful to understand the concept of localization but it is still a theoretical approach and sometimes boring and exhaustive. So let us find out a more practical approach by considering interesting example related to business approaches - practiced by some global business houses and how they are taking advantages of localization.
In order to understand how localization works, let us take the example of the McDonald's Corporation - the leading global foodservice retailer with more than 32,000 local restaurants serving more than 58 million people in around 130 countries each day. McDonald's presence in the global market is so prominent that it has become emblematic of globalization, sometimes referred to as the ‘McDonaldization’ of society. Now to achieve this status in international business arena, apart from delivering world class burger and service, McDonald's has implemented the basic concept of localization very effectively. Let us see how. McDonald's has found that, changes to their menus are a great way to globalize their brand without losing their identity. In order to make it possible, in Netherlands they will serve you Fritessaus instead of mayonnaise, in Canada you’ll be given locally-inspired Poutine instead of fries and in India our taste buds might become more sensitive when we look into the menu card and order something like McAlooTikki, Masala Grill Veg/Chicken or Chicken Maharaja Mac.
This is what localization is all about – Go Global By Going Local. We can now understand how it impacts the local consumer who is the ultimate key of the global market. Also considering the above McDonald's case we will try to clarify the differences in the terminologies like Localization, Translation and Transliteration. Let us take McAlooTikki as an example – in the English menu the company has not even translated the term in Indian language script, but the item name is very much localized and successfully presented in front of the Indian customers.
In this case instead of translation, a different approach of localization is used that is generally known as Transliteration. By definition, Transliteration is the conversion of a text from one script to another. McAloo Tikki is nothing but the transliterated form of the translated version of McPotato Roast. But any Indian food lover will agree on the fact that, the localized McAloo Tikki is far tastier than McPotato Roast, whereas the funny thing is that they are literally same.
LOCALIZATION – THE ‘WHY’ FACTOR – CAN’T READ, WON’T BUY
Now let us talk about why Localization should be a priority if we decide to grow our business beyond the barrier of some geographical border and to reach the global consumer with our products or services of any kind.
Over the past few decades, reports on surveys conducted by many leading market research groups have indicated a critical tendency of the global consumers, i.e. “Can’t Read, Won’t Buy”. Out of total surveyed consumers from all over the world, more than 70 percent of them said that they are more likely to buy products or services with information written in their native language. Hence it has become imperative that Localization makes products and services more accessible on a global front.
From our ancient civilization, language remains a barrier to the world functioning as a global village and economy. If effectively implemented, the localization approach can break this barrier to a maximum extent; at least it has become a truth for many business organizations over the past many decades.
ARE WE READY FOR THIS GLOBAL CHALLENGE?
Let us consider some facts revealed through the reports of some global surveys conducted on diversified groups of consumers from all over the world, that effectively illustrate the need to localize content for each target market:
- It would take 83 languages to reach 80 percent of all the people in the world, and over 7,000 languages to reach everyone.
- 56.2 percent of consumers say that the ability to obtain information in their own language is more important than the price.
- 74 percent of multinational enterprises believe it is either important or most important to achieve increased revenues from global operations.
- 95 percent of Chinese online consumers indicate greater comfort level with websites in their language
Now let us see some facts that are counter effects of the above facts:
- News, political statements, websites, movies, product literature, software, safety information, labeling, digital games and customer support are all translated every day in over 500 major language pairs worldwide.
- The worldwide language services market is growing at an annual rate of 7.4% and estimates for 2014 put the world market at some $39 billion
LOCALIZATION INDUSTRY AND GLOBAL BUSINESS
As a key component of Localization process, much work goes into translations. Words are translated into different languages; those words are tested for cultural relevance and understanding. Colors, images and symbols must be culturally appropriate. All these aspects are covered and undertaken by specialists from the localization and language industry.
It is the localization and language industry that helps organizations reach their target customers in the right language and cultural context. When you consider that less than 27% of the Internet is now in English, you can see why localization and language services are so important to companies worldwide.
The Localization industry consists of many different types of entities providing both outsourced language technology and services and in-house support within multinational companies. The industry is composed of:
- Technology Developers
Technology companies are a key element of the localization and language industry. Innovative companies are creating solutions to make localization a reality.
- In-house Localization & Translation Departments
Some multi-national companies have their own in-house teams that internally coordinate Localization & Translation strategy and implementation.
- Localization Service Providers (LSPs) & Translation Companies
Most of the multi-national companies work with outsourced localization service providers, to localize their products and services.
- Translators & Interpreters
Individual translators and interpreters are the core of the localization and language sector, often working as independent contractors and freelancers or as full-time staff.
LOCALIZATION AND MODULAR INFOTECH
 As a pioneer in the field of Indian language based software product development – Modular InfoTech Pvt. Ltd. has massively contributed in all the above fields of localization industry. Apart from being a Localization Technology Developer for almost last three decades, in 2003 Modular InfoTech started providing Localization & translation Service to its Indian as well as foreign clients. This new journey was started with the prestigious project of complete localization of Microsoft Windows XP and Office 2003 in 5 major Indian languages, directly awarded by Microsoft Corporation, USA. It’s been a complete decade; Modular InfoTech is continuing to provide its quality service in the field of Localization & translation to its renowned American, European, Asian and Indian clients. Presently based on our clients’ requirement we are providing language service in 13 major Indian languages – Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Konkani, Malayalam, Marathi, Odiya, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu. As a pioneer in the field of Indian language based software product development – Modular InfoTech Pvt. Ltd. has massively contributed in all the above fields of localization industry. Apart from being a Localization Technology Developer for almost last three decades, in 2003 Modular InfoTech started providing Localization & translation Service to its Indian as well as foreign clients. This new journey was started with the prestigious project of complete localization of Microsoft Windows XP and Office 2003 in 5 major Indian languages, directly awarded by Microsoft Corporation, USA. It’s been a complete decade; Modular InfoTech is continuing to provide its quality service in the field of Localization & translation to its renowned American, European, Asian and Indian clients. Presently based on our clients’ requirement we are providing language service in 13 major Indian languages – Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Konkani, Malayalam, Marathi, Odiya, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu.
LANGUAGE TRANSLATORS – THE VITAL ASSETS OF LOCALIZATION SERVICE
With the massive evolution of software technology, Localization & translation Service is also experiencing substantial technology advancement and it is helping this IT Enabled Service to manage and implement its processes in order to provide business solution more and more effectively. Though these modern language services are managed by computer and internet, it is obvious that, they also require human intervention. As mentioned earlier also, in order to provide reliable Localization & translation service we require many good, hardworking, committed translators. Being the vital resource of Localization industry we consider our translators as our assets, but at the same time this job brings great responsibility for them also. It is indeed a serious, committed and interesting profession if we consider and accept it in that way.
The following three vital qualities or abilities are required for the translators, regardless whether they have any relevant experience or they are completely freshers:
-
Very good understanding in his/her mother tongue to clearly express the idea in that language
-
Good understanding of English to understand the source content that needs to be translated
- Knowledge of computer operations, essentially Microsoft Windows, MS Office and Internet
With these qualities, you can always look forward to this as your profession. This profession can offer you much flexibility in your job profile. The best parts are:
- Anyone having the above abilities can do the translation work
- Resources from any Indian states can do the job from their home
- Resources can give their spare time or full time depending upon their availability
This article is going to end in the next few lines but we hope that it will seal the beginning of our journey with a powerful thrust towards a brighter future. After reading this, even if a single reader gets inspired and takes a positive step towards achieving a successful career in localization industry, we will think that our effort has been successful.
Though our Indian localization industry has still not achieved the maturity as compared to the European and other Asian countries, we will hope that in the coming years this subcontinent will stand tall and we will prove that like in all other fields, Indian localization industry is just as strong as the other countries – and together we will take the challenge and we will not allow it to merely become our legacy.
Localization Group, Modular Infotech
Mobile - +91 93701 46488
E-mail:kartiki@modular-infotech.com |
